
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
3 Key Laboratory of Transparent and Opto-functional Inorganic Materials, Artificial Crystal Research Center, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
4 School of Physics and Astronomy, Yunnan University, Kunming 650091, China
The anisotropy of thermal property in an crystal is investigated from the temperature of 293 to 573 K. Based on the systematical study of thermal expansion, thermal diffusivity, and specific heat, the thermal conductivity in crystals orientated at (100), (010), (001), and (406) is calculated to be 3.46, 2.60, 3.35, and , respectively. The laser output anisotropy of a continuous-wave (CW) and tunable laser is characterized, accordingly. A maximum output power of 6.09 W is achieved in the crystal with (010) direction, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 48.56%. The tuning wavelength range in the crystal orientated at (100), (010), and (001) is 68, 67, and 65 nm, separately. The effects of thermal properties on CW laser performance are discussed.
anisotropy thermal property tunable laser Yb,Nd:Sc2SiO5 crystal Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(4): 041405
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2 College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
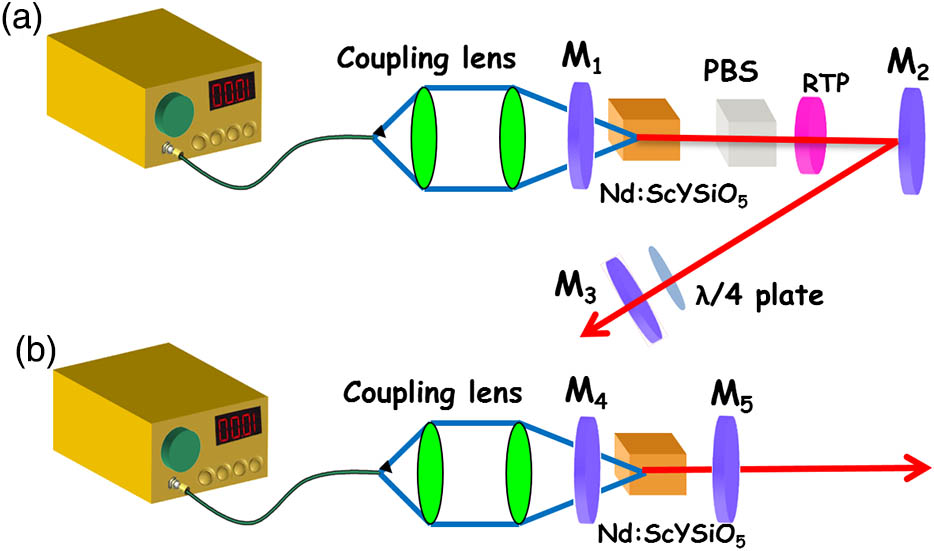
With a Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal, a high peak power electro-optically Q-switched 1.0 μm laser and tri-wavelength laser operations at the 1.3 μm band are both investigated. With a rubidium titanyle phosphate (RTP) electro-optical switcher and a polarization beam splitter, a high signal-to-noise ratio 1.0 μm laser is obtained, generating a shortest pulse width of 30 ns, a highest pulse energy of 0.765 mJ, and a maximum peak power of 25.5 kW, respectively. The laser mode at the highest laser energy level is the TEM00 mode with the M2 value in the X and Y directions to be Mx2 = 1.52 and My2 = 1.54. A tri-wavelength Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal laser at 1.3 μm is also investigated. A maximum tri-wavelength output power is 1.03 W under the absorbed pump power of 7 W, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 14.8%. The properties of the output wavelength are fully studied under different absorbed pump power.
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 111403
1 甘肃农业大学食品科学与工程学院, 甘肃 兰州 730070
2 甘肃省功能乳品实验室, 甘肃 兰州 730070
3 中国农业大学教育部功能乳品重点实验室, 北京 100083
4 中国农业大学北京食品营养与人类健康高精尖创新中心, 北京 100083
酪蛋白酸钠作为一种良好的乳化剂和乳化稳定剂, 对乳饮料品质具有重要的作用。 蔗糖作为甜味剂, 可以提高乳饮料的口感。 但酪蛋白结构和性质很容易受到其所处的微环境的影响, 为了分析蔗糖对酪蛋白酸钠结构及其乳化性的影响, 利用荧光光谱技术探讨了酪蛋白酸钠荧光光谱和表面疏水性的变化, 利用动态光散射技术分析了酪蛋白酸钠乳液液滴流体力学直径的变化, 利用Turbiscan光谱学稳定性测试评价了酪蛋白酸钠乳液的背散射光强度变化以及稳定性指数(TSI)。 结果表明: 蔗糖会使酪蛋白酸钠发生内源荧光猝灭, 猝灭速率常数KS<2.0×1010 L·mol-1·s-1, 属于动态猝灭, 未形成稳定的基态配合物, 表明两者仅以较弱的氢键和疏水相互作用结合。 酪蛋白酸钠的表面疏水性显著增强(p<0.05), 部分酪蛋白酸钠聚集程度增加, 形成了可溶性聚集体。 随着蔗糖浓度的增加, 酪蛋白酸钠乳液流体力学直径增大, 是高压均质时蛋白聚集体在油水界面上优先吸附的结果。 背散射光强度结果显示随着蔗糖浓度的增加, 乳液越不易产生分层、 浓度变化、 乳滴迁移等不稳定性现象。 稳定性指数显著增大(p<0.05), 乳液稳定性增强。
蔗糖 酪蛋白 表面疏水性 乳化性 乳化稳定性 Sucrose Sodium caseinate Surface hydrophobicity Emulsibility Emulsion stability 光谱学与光谱分析
2017, 37(10): 3127





